Wall Colmonoy announces the release of Colmonoy® 686, a Ni-Cr-Mo-W superalloy. Colmonoy® 686 is a nickel-based powder specifically developed to combat the extreme high temperature and corrosion experienced in modern waste-to-energy and biomass plants.
In this type of environment, tube surface temperatures can reach in excess of 550°C, placing enormous strain on waste-to-energy and biomass parts, such as boiler tubes, water-walls and superheaters due to the presence of chlorine and sulphur, which form corrosive compounds.
Where there is an existing nickel-based alloy in use, Colmonoy® 686 can easily be integrated and is fully compatible with alloys such as Inconel™ 625 or Colmonoy® 625 without posing an operational risk.
Colmonoy® 686 is primarily applied via laser cladding, though the alloy can also be applied by PTA or HVOF. Colmonoy® 686, laser deposited, can achieve a nominal hardness of 99HRB.
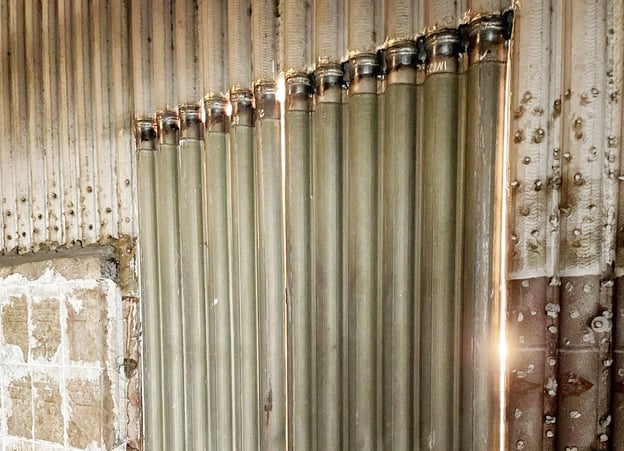 Laser-cladded tube panels installed in the combustion chamber of a waste-to energy plant. Image courtesy of Häuser & Co.
Laser-cladded tube panels installed in the combustion chamber of a waste-to energy plant. Image courtesy of Häuser & Co.
Our customers asked for an alloy that performed even better than Colmonoy® 625 for resistance to hot gas corrosion in high temperature environments. We developed Colmonoy® 686 with a pitting resistance equivalent number of 81!
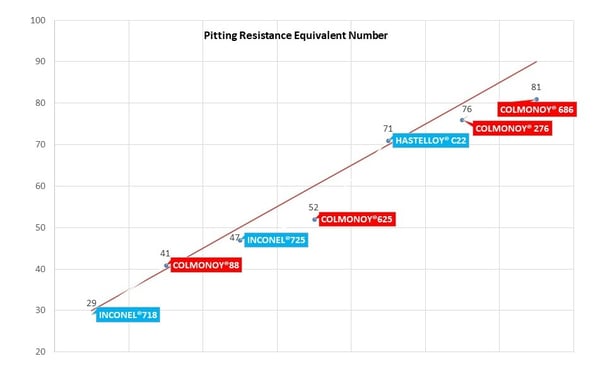
Colmonoy® 686 is currently in selected European Biomass and Waste to Energy Plants.
With such high pitting resistance and higher molybdenum and chromium levels than existing alloys, Colmonoy® 686 can provide superior protection against hot-gas corrosion.
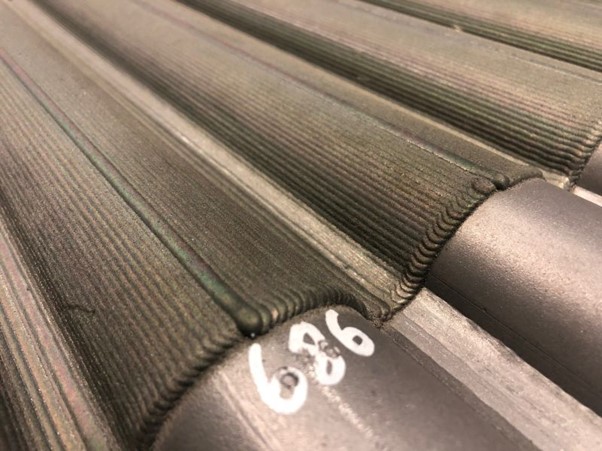 Membrane water-wall in a Waste-to-Energy Plant with Colmonoy® 686 coating, applied by laser cladding. Image courtesy of Häuser & Co.
Membrane water-wall in a Waste-to-Energy Plant with Colmonoy® 686 coating, applied by laser cladding. Image courtesy of Häuser & Co.
For more information or to arrange a trial



